La animal cell It is one of the units that are basic and fundamental within the existence of living beings and as such can be found in their tissues. Although they are microscopic, they are formed by a fairly complex structure that should be known.
The animal cell is said to be a type of eukaryotic cell, that is, those with a well-organized cell nucleus. Furthermore, it is enveloped by the so-called nuclear envelope and many other parts. So, we mention each and every one of them, as well as their various characteristics.
What is the animal cell
Broadly speaking we can define animal cell as a unit or type of eukaryotic cell, which is vital for the animals or beings of 'Animalia'. This type of cells will be in charge of carrying out processes such as producing energy or the proper functioning of metabolism. So they will be found in the tissues. Since the cells that perform the same functions are usually united to form the so-called tissues. In turn, the tissues will be organized to give rise to the organs and these to the systems. A set of basic units that are all of the most necessary and that make up living beings.
Structure and parts of the animal cell
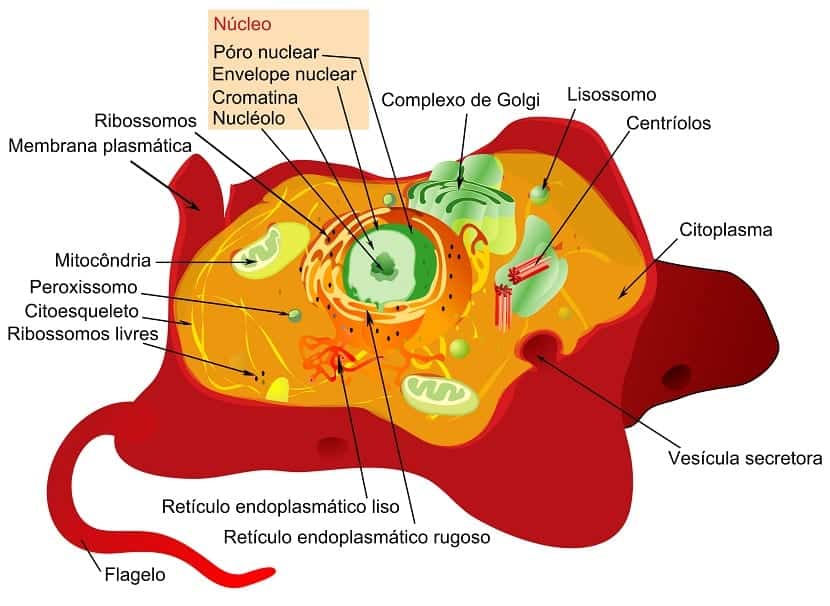
It should be mentioned that the fundamental parts of the animal cell are three main: the cell envelope, the cytoplasm and the cell nucleus. Although within some of these parts, we find cellular organelles or structures that are also worth mentioning, since they continue to be vital parts of said cell.
- La cell envelope which is made up of the cell membrane. Although it is also often known as the plasma membrane. It is a kind of layer that will delimit the entire cell. They are two sheets of protein and glycolipids that will maintain the balance inside. In fact its function is to control the entry or exit of some substances.
- El cytoplasm it is part of the living material of the cell. That is, the interior of the cell between the nucleus and the membrane. It is made up of elements as well as chemicals. Water, proteins, carbohydrates and lipids will be what we find in it.
- La mitochondria it is a tiny structure that has a double membrane. Its function will be to convert nutrients into energy, which will be called cellular fuel.
- El Lysosome It is a kind of sac that is responsible for the so-called 'cellular digestion'. That is, of the processes or reactions that occur in a cell. They are found in all animal cells and can be variable. They have a spherical shape and are surrounded by a simple membrane.
- El Golgi apparatus it can be found in animal cells but also in plant cells. It is the order to distribute the proteins.
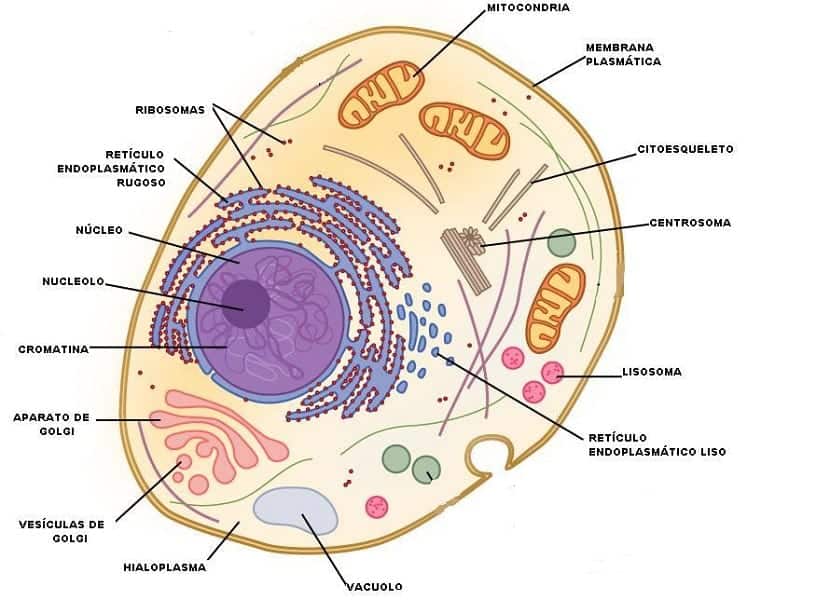
- El endoplasmic reticulum It is a compound of membranes that are shaped like flat sacs and connected to each other. Its function is to organize the membranes according to the different tasks they perform. We can find the endoplasmic reticulum smooth or rough.
- El Centriole it is an organelle that has a cylindrical shape. They are involved in cell division, maintaining the perfect shape of each cell.
- Undoubtedly, the nucleus is another of the most important parts of every cell, both vegetables and animals. It is spherical and within it both DNA molecules and proteins are organized into chromosomes.
- The nucleoplasm is separated from the rest of the cell by a double layer membrane where the nucleoplasm goes.
- Chromatin is the set of DNA as well as the proteins that are found in the part of the nucleus of the cells and that constitute the genome of the cells.
- When we talk about one of the core regions, then we have to mention the nucleolus. It is who regulates the cell cycle, responsible for aging.
Animal cell types
It is said, as a general rule, that there may be more than 200 types of animal cells. Within them, a classification of the most important or relevant can be made.
- Blood cells: We meet the Red blood cells. In charge of carrying oxygen to the different organs. On the other hand, there are the white blood cells that will protect against any infection or disease.
- Muscle cells: Within the muscles we are going to find three different types. The skeletons that are attached to the bone and help in its movements. On the other hand we have the smooth ones, which cause involuntary movements and the cardiac ones.
- Epithelial: They are responsible for covering the outside, both of the body and organs.
- All the nerve cells they communicate with each other and form the nervous system. Among them are the sensitive, association and motor.